PREXISE-D
- SCF/c-KIT pathway as a drug target
- Benefits of Targeting SCF/c-KIT in ophthalmology
(in comparison of VEGF)
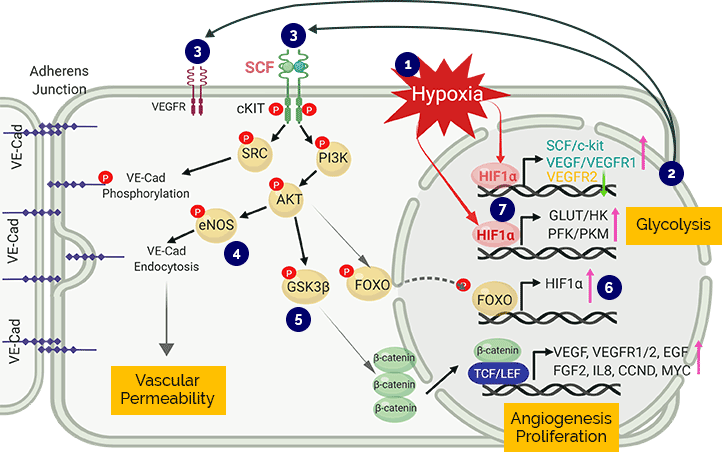
1Hypoxia stabilizes HIF-1α
2HIF-1α stimulates the expression of angiogenic factors including SCF/c-KIT and VEGF/VEGFR, and activates glycolytic metabolism of endothelial cells
3SCF/c-KIT and VEGF signal transductions are respectively activated
4Phosphorylation of VE-Cadherin provokes its internalization, increasing permeability of vascular endothelial cells
5GSK3 phosphorylation augments β-catenin which localizes into the nucleus, expressing angiogenic and proliferative factors
6Phosphorylated FOXO translocates to the nucleus, boosting up the expression of HIF-1α
7Increased expression of HIF-1α creates a vicious cycle of enhanced angiogenesis
SCF/c-KIT pathway as a drug target
Stem cell factor (SCF) mediates multiple cellular responses by binding to and activating the receptor tyrosine kinase, c-KIT (KIT or CD117). Since its discovery in 1987, c-KIT has been known as an oncogene, and SCF/c-KIT signaling is required for the development of hematopoietic stem cells, melanocytes, and germ cells.
In 2012, our team first made a novel discovery that SCF/c-KIT signaling is one of the key drivers of angiogenesis, including tube formation, migration, and proliferation of endothelial cells. Hypoxia stimulates the expression of c-KIT, which in turn enhances the expression of VEGF, IL-8, and cyclin D1, resulting in the increased neovascularization. Besides, the activation of c-KIT signaling induces vascular permeability of endothelial cells, which is critical to the development of edema in patients.
To date, VEGF is the most well-known angiogenesis target. However, we have verified that SCF/c-KIT, independently of VEGF, induces neovascularization and vascular permeability, which are not mediated by anti-VEGF drugs. This finding could be an answer to the reason why there are up to 40% of anti-VEGF treatment-fail patients exist. For further information about SCF/c-KIT pathway as a novel ophthalmology target, please see our publication here.
Also, the c-KIT mutation is reported to be widely engaged in the pathogenesis of gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST), Leukemia (CML & AML), small cell lung carcinoma (SCLC), glioblastoma (GBM) and mastocytosis. The activating mutation of c-KIT is known to induce resistance to imatinib (Gleevec) in cancer patients.

 ddd
ddd